The Histology Research Facility offers a wide array of routine and specialized stains featured below:
All of the stain images below are images from slides stained in house by the Histology Research Core Facility
Additional specialized stains, if not listed below, are available upon request. Please contact Ashley Ezzell to discuss a project quote and protocol details.
Routine
Hematoxylin and Eosin, commonly reffered to as H&E, is considered a routine stain in identifying the morphological structures within a tissue section. The nuclei in this stain are stained a blue-purple hue from the hematoxlyin. Eosin is used as a counter stain to mark cytoplasm and muscle fibers in varying pink hues.
Multiple Structures
Movat’s Pentachrome is a complex stain that highlights fibrin, mucin, and collagen in a tissue section. The cellular structures on a slide will be stained as follows: nuclei and elastic fibers black, fibrin intense red, muscle red, collagen and reticular fibers yellow, and ground substance mucin blue.
Oxone-Aldehyde-Fuschin-Halmi Stain
The Oxone-Aldehyde-Fuschin-Halmi stain is used to primarily visualize oxytalan fibers and connective tissue within periodontal tissue. Oxytalan fibers are libeled a deep violet, keratin, tooth pulp, mast cells, and basement membranes are labeled a lighter purple, nuclei are a blueish-brown, epithelial cells are green, and collagen is a green-greenish yellow.
Lipid
Oil Red O stain is used to highlight lipid morphology within a tissue section. This stain can only be performed on frozen sections for optimal staining. Within the stain, the lipids are stained an orange to brilliant red hue and hematoxylin is used to stain nuclei a blue to purple hue.
Connective Tissue
Picrosirius Red stain is used to highlight connective tissue, specifically collagen, within a tissue section. Collagenous fibers within a tissue sample are stained a vibrant red while other elements of the tissue are stained yellow hues. In plain polarized light, collagen fibers are manifested in a striking manner as vivid orange-red bands against a black background
Mason’s Trichrome stain is used to highlight connective tissue fibers in a tissue section. Collagen fibers are stained a blue hue, nuclei a blue-black, and cytoplasm, keratin, and muscle fibers a range of pink to red hues.
AZAN Trichrome stain is used to highlight collagen fibers within a tissue section. The following are the hues that each cellular structure is stained: nuclei and erythrocytes are stained red, muscle is stained orange, glia fibrils reddish, mucin blue, reticulum dark blue, glomerular stroma dark blue, and collagen dark blue.
Combined Massons Elastin stain is primarily used to highlight connective tissue fibers within a tissue sample. In this stain, elastic fibers and nuclei are stained black, collagen and mucin green, and keratin, cytoplasm, muscle fibers red.
Neural
Cresyl Echt Violet (CEV) & Luxol Fast Blue (LFB)
The Cresyl Echt Violet, also known as CEV, stain is used to highlight nissl substances and nuclei. The nissl substances and nuclei are stained purple, whereas the background remains clear.
Luxol Fast Blue stain is used to mark the myelin within a cell. In this stain, myelin is stained a greenish blue hue and cells are stained a pink to violet hue.
Glycogen & Mucins
Safrananin O is used in the detection of cartilage, mucins and mast cells on formalin fixed, paraffin embedded tissue. This stain can also be completed on frozen sections. The cartilage and mucin in this stain will be stained orange to red, the nuclei will be stained black, and the background will be stained green.
PAS stain is performed to highlight glycogen and goblet cells within a tissue section. The glycogen in this stain will appear rose to red on a slide, and mucosubstances will be stained blue. Hyaluronic acid, sialomucins and all but most strongly acidic mucosubstances will stain blue.
PAS stain is performed to highlight glycogen and goblet cells within a tissue section. The glycogen in this stain will appear rose to red on a slide, and nuclei will be stained a blue-violet hue from the hematoxylin.
Minerals
Von Kossa is performed to highlight mineralization within a tissue section. The structures in a tissue section are stained as follows: calcium salts are stained black, nuclei red, and cytoplasm pink. If this stain is performed with Light Green, the calcium salts will be stained black, the nuclei darker green, and the cytoplasm green.
Prussian Blue
Prussian Blue stain is used to highlight iron deposits within cellular structures. In this stain, nuclei and hemofuchsin are stained bright red, hemosiderin (iron) blue, and the background structures pink). If iron deposits within a tissue section are low, DAB can be used to enhance the stain and distinguish any iron within a structure.
Basement Membranes
Jones Methenamine Silver is used to stain basement membranes within a cellular structure. In this stain, the nuclei are stained blue, cytoplasm/background pink, and basement membranes are stained black.
Mast Cells
Toluidine Blue is used to distinguish mast cells within a tissue sample. In this stain, mast cells are stained a violet to reddish purple and the background is stained blue.
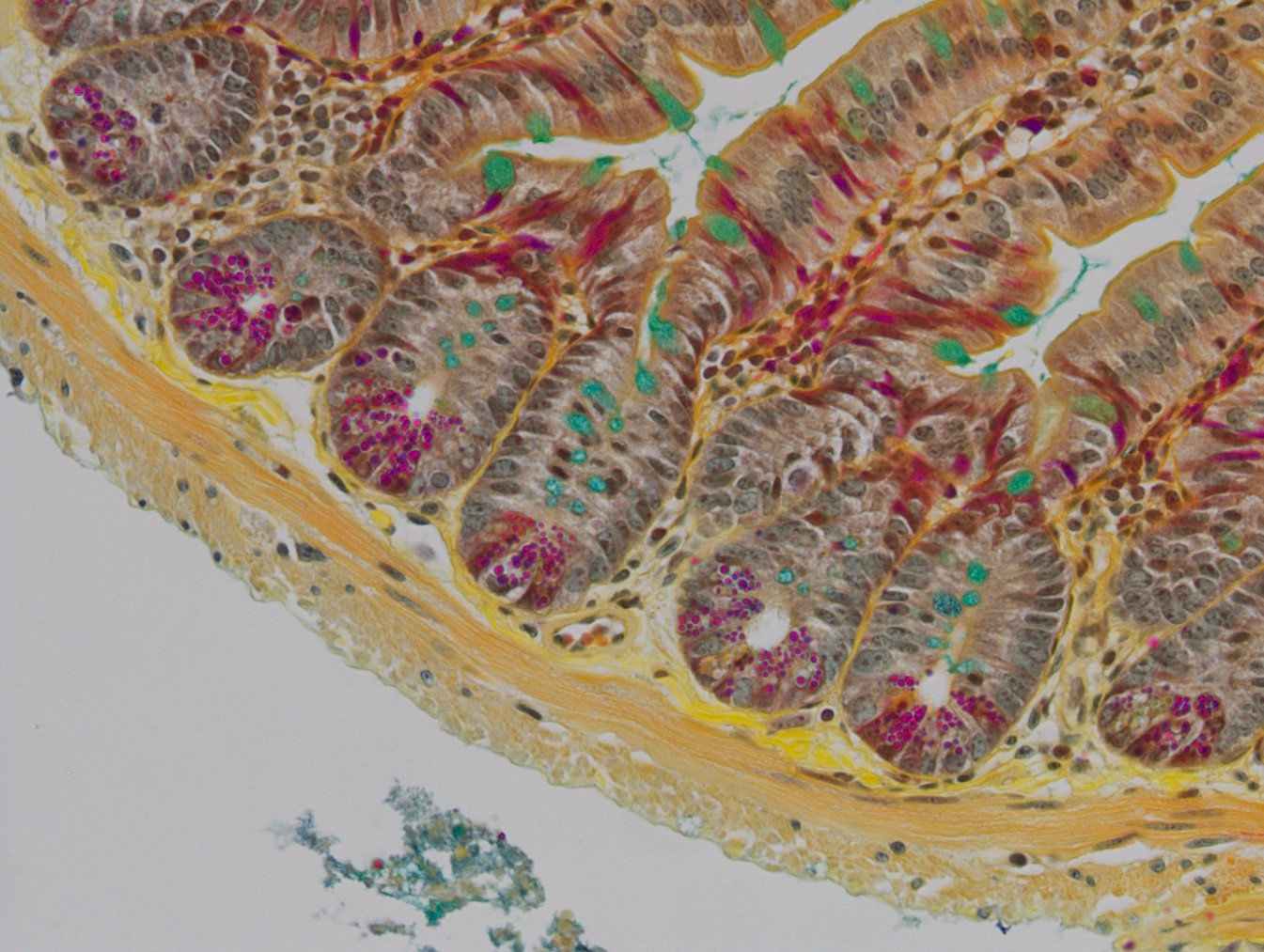
Paneth Cells
Phloxine/Tartrazine/Alcian Blue
Mature paneth cells are bright red, while immature paneth cells stain a golden yellow color. Goblet cells are stained pale-light green.
Fungus and Bacteria
Chromic Acid Schiff (CAS)
CAS is very similar to PAS but is specifically used to stain fungi. The periodic acid step in PAS is replaced by chromic acid. This reduces background staining of basement membranes, collagenous and reticular fibers so that only the areas of highest polysaccharide content (fungal walls) are stained. In this example, the fungus has a brown exterior with a reddish pink interior.
The Ziehl-Neelsen stain distinguishes acid-fast organisms and is mainly used to visualize Mycobacteria and acid-fast fungi such as Histoplasma. In this stain acid-fast organisms stain bright pink with a methylene blue counterstain.